| AMMONIUM SUCCINATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 2226-88-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 218-759-3 | |
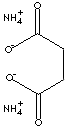
| FORMULA | H4NOCCH2CH2COONH4 | |
| MOL WT. | 152.15 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2917.19 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | Succinic acid, diammonium salt; | |
| Diammonium Succinate; Butanedioic acid, diammonium salt; Succinato de diamonio (Spanish); Succinate de diammonium (French); | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystal | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Soluble | |
| pH | 7 - 9 (5% sol) |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Succinic Acid (Butanedioic Acid) is a dicarboxylic acid of four carbon atoms. It occurs naturally in plant and animal tissues. It plays a significant role in intermediary metabolism (Krebs cycle) in the body. Krebs cycle (also called citric acid cycle; tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a sequence process of enzymatic reaction which a two-carbon acetyl unit is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water to provide energy in the form of high-energy phosphate bonds. Succinic acid is a colourless crystalline solid with a melting point of 185 -187 C; soluble in water; slightly dissolved in ethanol, ether, acetone and glycerine; not dissolved in benzene, carbon sulfide, carbon tetrachloride and oil ether. The common method of synthesis of succinic acid is the catalytic hydrogenation of maleic acid or its anhydride. Carboxylic acid can yield acyl halides, anhydrides, esters, amides, and nitriles for the application of drug, agriculture, and food products, and other industrial uses. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystal | |
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min |
|
|
FREE ACID |
0.5% max |
|
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
7.0% max |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||